Manage Explore Next Generation Firewall
Want to set up your own personalized firewall protection? We’ll explain you the basics to set up your Explore Next Generation Firewall.
Explore Next Generation Firewall uses Palo Alto Networks’ firewall, application control, advanced threat protection, IPS, URL filtering and SSL teleworking. Download the PDF manual(PDF, 4 MB) .
Get started
We’ll explain you how to log in and give an overview of the most important features.
Contextual help is also available in the interface of your firewall by pressing  .
.
Policies, objects & security profiles
Policies are controls that enable you to allow, restrict, and track traffic based on the application, user, user group or service (port and protocol). You can define your security rules, but also NAT, application override and authentication policies here.
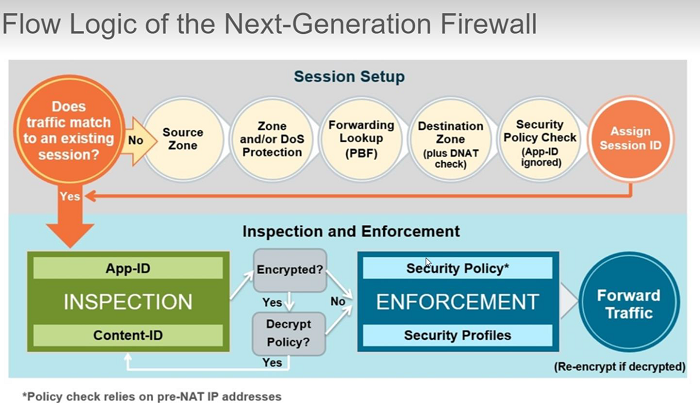
Your firewall uses packet inspection and an application signature library to distinguish applications (by protocol or port) and to identify malicious applications using nonstandard ports.
For maximum safety, use security policies for specific applications or application groups rather than, for example, a single policy for all port 80 connections. For each application, you can block or allow traffic based on source and destination zones and addresses (IPv4 and IPv6). Each policy can also have security profiles against viruses, spyware, etc.
Objects are elements you can use in your policies or security profiles:
Security profiles are objects we can add on top of the standard firewall inspection. They allow more control and additional security checks to be performed on network traffic.
As best practices, it is recommended to implement the predefined default security profiles. These default security profiles are applied to the standard initial configuration and follow this naming convention ‘Sec_Prof_xx_PM’ (where ‘xx’ is replace by the profile type: AV for antivirus, VP for vulnerability protection, etc.). Those profiles can be applied in the Objects tab under Security Profiles, either individually or as a group profile. Your firewall offers several types of security profiles:
Teleworking
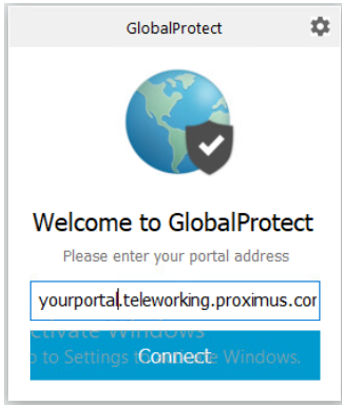
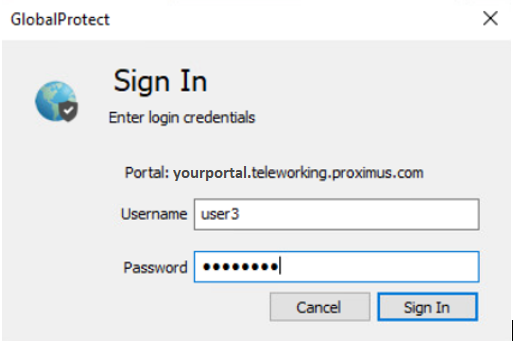
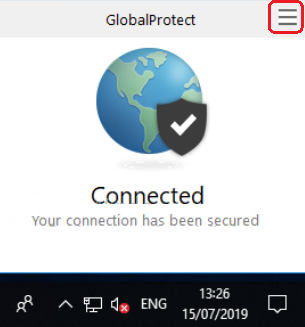
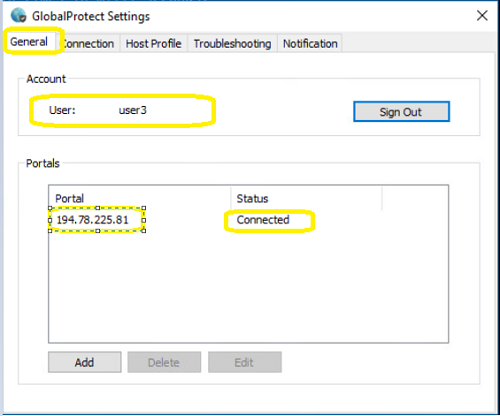
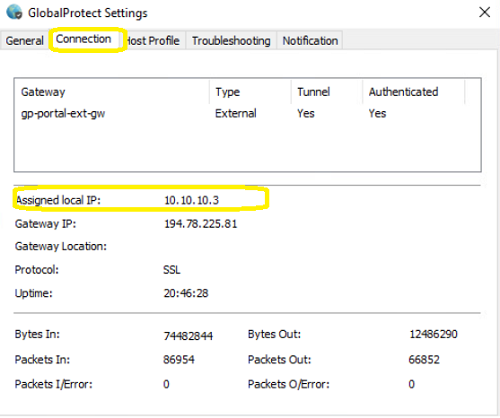
If you have subscribed to this service, you can provide remote access to the users on your network using the GlobalProtect software.
This service is proposed in 2 flavours:
- Local users: your teleworking users and passwords are stored locally on the Explore Next Generation Firewall platform, per pack of 5 simultaneous teleworkers.
- LDAP/AD: your teleworking users and passwords are defined on an Active Directory. An additional configuration between the firewall and your Active Directory server is required. This flavour is not part of the self-managed package and must be configured with the help of an Explore engineer. If you have any questions about this, contact us .
If you have the 1st flavour, you will find all the information to manage your teleworking users and passwords below.
Change or reset your firewall password
Your password can only be changed if you are already logged in. If you can’t log in, contact us to reset your password.
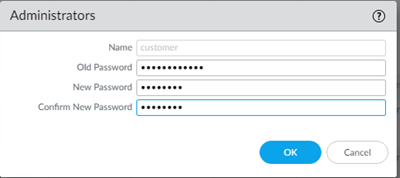
To change your password, follow these steps:
- Click on customer at the bottom of the page.
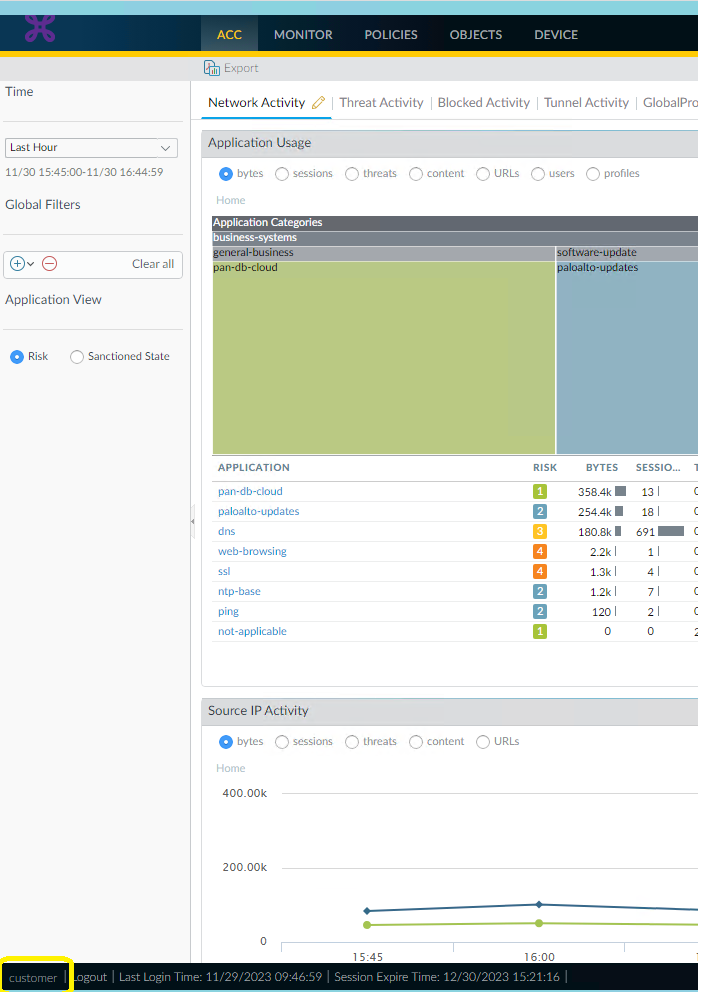
- You will have to choose a new password:
- In the field Old Password, enter current password.
- In the field New Password, choose a password of min. 8 characters containing at least 1 uppercase, 1 lowercase, 1 special and 1 numeric character.
- In the field Confirm New Password, repeat your chosen password and click on OK.
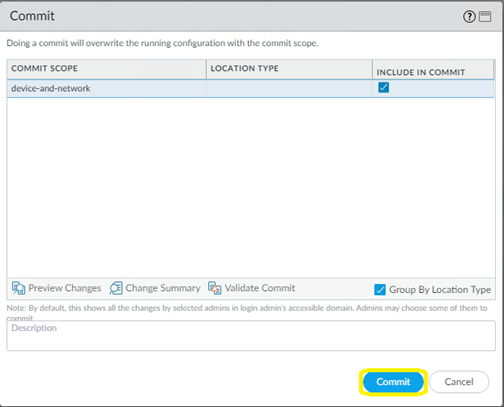
- Click on Commit on top of the page to confirm your changes.

- Click on Commit again in the pop-up window that appears.
Your login and password can only be used by you. Proximus has seperate credentials to access the Firewall. If you lose your password, you must contact the Service Desk to request a reset of your password.
Your access rights to features on the firewall
Download an overview of the access rights(PDF, 498 KB) with a list of the features you can see, edit and cannot see on your firewall.
Consultancy and Training
Customers such as you can benefit from our consulting services and training:
Get Help
As a client you can count on us for help via: